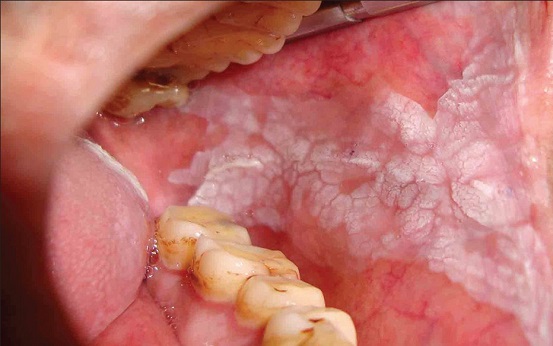
Oral Submucous Fibrosis
Oral submucous fibrosis is a chronic debilitating disease of the oral cavity characterized by inflammation and progressive fibrosis of the submucosal tissues (lamina propria and deeper connective tissues). Oral submucous fibrosis results in marked rigidity and an eventual inability to open the mouth
Oral submucous fibrosis is a chronic, complex, premalignant (1% transformation risk) condition of the oral cavity, characterized by juxta-epithelial inflammatory reaction and progressive fibrosis of the submucosal tissues (the lamina propria and deeper connective tissues). As the disease progresses, the jaws become rigid to the point that the person is unable to open the mouth. The condition is remotely linked to oral cancers and is associated with areca nut or betel quid chewing, a habit similar to tobacco chewing, is practiced predominantly in Southeast Asia and India, dating back thousands of years.
Dried products such as paan masala and gutkha have higher concentrations of areca nut and appear to cause the disease.